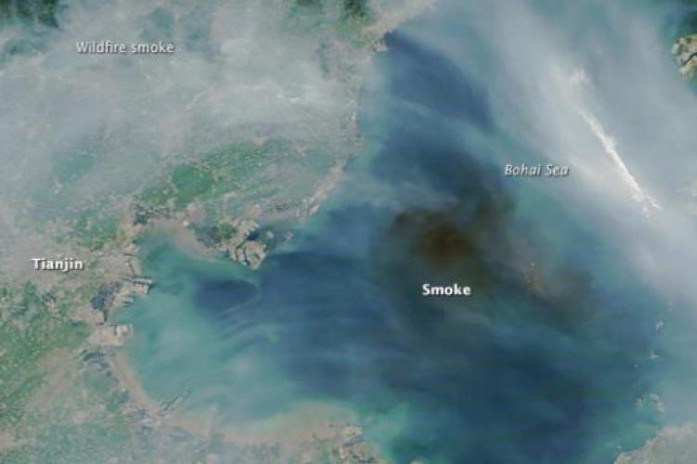
On August 12 explosions occurred at a warehouse, where loads of highly toxic substances, largely sodium cyanide, were being kept at Tianjin port city. A day later, the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation used eight of its satellite constellation to assess the rescue and damage operations during the emergency response.
Moreover, the National Satellite Meteorological Center also put its weather satellites to use during the disaster. The weather satellites captured images so as to discover fires in the blast zones and send them to government departments, helping in damage assessment and rescue activities.
An unnamed space expert asserted that, “Earth observation satellites have many types of imaging devices, so compared with other observation platforms they are more resistant to bad weather and can obtain high-definition pictures through smoke caused by the blasts.” Read here for more.
Cross Reference
UN-SPIDER